Angle grinder cut-off wheels come in various types and thicknesses tailored for different materials and cutting needs. Thinner wheels (0.04 to 0.045 inches) offer precise cuts, while thicker ones enhance durability for heavy-duty tasks. Selecting the right grain type—ceramic for aggressive cuts or aluminum oxide for general use—is essential for performance. Always prioritize safety by wearing protective gear and ensuring the wheel’s RPM matches your grinder. There’s more to mastering their use effectively, so keep exploring!
Understanding Cut-Off Wheels: Types and Their Uses

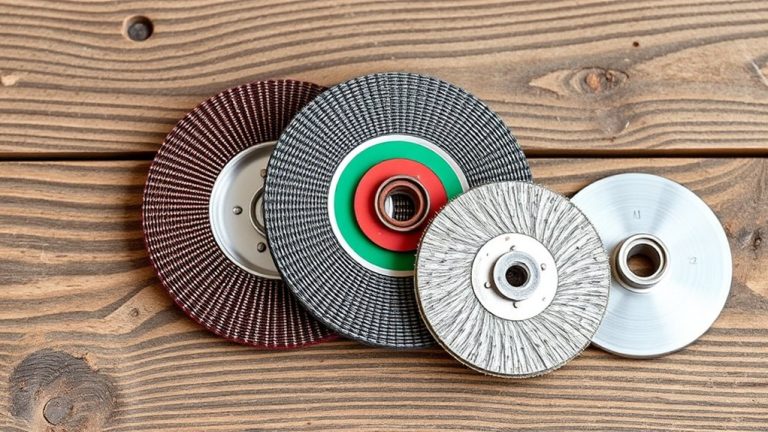
When you’re looking to make precise cuts in metal, understanding the different types of cut-off wheels is essential for achieving the best results. The Type 1 wheel, a flat configuration, is perfect for general all-purpose cutting, while the Type 27 wheel offers better visibility and flush cutting in tight spaces. The thickness of the cut-off wheel also plays a critical role; thinner wheels, typically ranging from 0.04 to 0.045 inches, provide faster and more precise cuts but are more susceptible to shattering. On the other hand, thicker wheels enhance durability but may compromise precision. Choose the right abrasive grains for your task—aluminum oxide for versatility, ceramic for challenging metals, and zirconia alumina for heavy-duty applications. Always wear safety gear to protect yourself from flying debris, ensuring you handle these tools with care for peak performance and safety.
The Impact of Grain Type on Cutting Performance
When choosing a cutoff wheel, understanding the impact of grain type is essential for ideal cutting performance. Each grain—ceramic, zirconia alumina, and aluminum oxide—offers different advantages, affecting speed, lifespan, and cut quality. Selecting the right grain type based on your specific application can greatly enhance your results and prevent unnecessary frustration.
Grain Types Overview
Choosing the right grain type for your angle grinder cutoff wheel is essential for achieving ideal cutting performance. In this grain types overview, you’ll find various options tailored to specific tasks. Ceramic grains excel in aggressive cutting on hard metals, offering a superior lifespan under light pressure. Zirconia alumina is perfect for heavy-duty jobs, ensuring efficient material removal at a low cost-per-cut. Aluminum oxide, the most common type, provides balanced durability and affordability for diverse cutting tasks. Finally, silicon carbide shines in cutting non-ferrous materials and softer metals due to its sharpness. Remember, the grain type greatly impacts cutting speed, lifespan, and cut quality, so match it carefully to the material you’re working with.
Performance Comparison Among Grains
Understanding how different grain types affect cutting performance is essential for maximizing efficiency and achieving desired results. Each grain type plays an important role in cutting efficiency and longevity, influencing how well your wheels perform.
| Grain Type | Performance | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Grains | Sharp edges, fractures easily | Aggressive cutting |
| Zirconia Alumina | Durable, low cost-per-cut | Heavy-duty tasks |
| Aluminum Oxide | Versatile, good cut rates | Various materials |
Ceramic grains excel in speed and lifespan, while zirconia alumina is robust for tough jobs. Aluminum oxide is the most common, offering decent performance at a lower cost. Choosing the right grain type is essential to avoid issues like disc glazing or premature wear.
Selecting Appropriate Grain Type
Selecting the right grain type is essential for maximizing cutting performance and achieving the best results. The choice of abrasive grain directly impacts your grinding discs’ efficiency. Ceramic grains excel at cutting through hard materials, offering sharp edges that fracture under pressure for faster cuts and longer lifespans. For heavy-duty tasks, zirconia alumina grains provide exceptional durability and a favorable cost-per-cut ratio. Although aluminum oxide is the most common type, it may not perform as well on tougher materials. Additionally, grit size plays a significant role; lower numbers yield coarser cuts, while higher numbers produce finer finishes. As a result, selecting the appropriate grain type based on your workpiece material is essential to minimize glazing and guarantee optimal cutting speed and quality.
Matching Your Wheel to the Material Being Cut
When you’re cutting various materials, matching the right wheel to the job is crucial for both performance and safety. Using the appropriate cutting wheels can greatly enhance your results and prevent hazards.
Choosing the right cutting wheel for your material is essential for optimal performance and safety.
- For steel and stainless steel, opt for thick (3mm) coarse to medium cut-off wheels for durability.
- When working with thin aluminum sheets, choose fine to medium grinding discs to avoid melting.
- For thick aluminum, stick to coarse to medium abrasive cut-off wheels for clean cuts.
- If you’re tackling tile or masonry, select coarse diamond blades or grinding discs based on the material’s thickness.
Always verify that the wheel you choose aligns with the material’s specific requirements and the angle grinder’s RPM compatibility for safe operation. This attention to detail will lead to better results and a more enjoyable cutting experience.
Choosing the Right Cut-Off Wheel Thickness for Your Needs

Choosing the right cut-off wheel thickness is vital for achieving ideal cutting performance and safety. When selecting the correct thickness for your cut-off wheels, consider the material you’re working with. Thinner wheels (0.04 to 0.045 inches) excel in metal cutting, providing precise cuts in stainless steel or thin metal sheets. However, they’re more prone to shattering, so handle them carefully. For general applications, a thickness of 0.045 inches strikes a balance between cutting speed and durability. If you need to tackle heavier materials, opt for thicker wheels (around 0.060 inches) to guarantee longer lifespan and increased durability. Keep in mind that kerf size affects both cutting speed and wear rate; a narrower kerf allows for faster cutting but may wear out quicker. Ultimately, selecting the right thickness is vital to achieving efficient and safe results in your projects.
Stay Safe: Tips for Using Your Angle Grinder Cut-Off Wheels
Using an angle grinder with cut-off wheels can be efficient, but safety should always be your top priority. By following these essential tips, you can guarantee a safer cutting experience:
Using an angle grinder with cut-off wheels is effective, but prioritizing safety is crucial for a secure cutting experience.
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles and gloves, to guard against flying debris.
- Verify that the cut-off wheel’s RPM rating matches or exceeds your grinder’s RPM to avoid wheel breakage.
- Securely clamp the workpiece to prevent movement, which enhances cutting accuracy and safety.
- Avoid applying excessive pressure on the cut-off wheel; this minimizes the risk of shattering and extends the wheel’s lifespan.
Also, maintain a safe distance from flammable materials and have a fire extinguisher nearby, as sparks generated during cutting can ignite nearby substances. By adhering to these safety measures, you can enjoy the benefits of angle grinders while minimizing risks.
Mistakes to Avoid With Cut-Off Wheels
When using cut-off wheels, it’s essential to choose the right wheel type for your material; using the wrong one can lead to poor performance and damage. Don’t forget your safety gear, as neglecting it can result in serious injuries. Finally, applying excessive pressure is a mistake that can cause premature wear on the wheel and ruin your cuts, so maintain a steady hand for the best results.
Choosing Incorrect Wheel Type
Selecting the wrong type of cut-off wheel can lead to significant issues, such as inefficient cuts or even dangerous accidents. To avoid these pitfalls, consider these key points:
- Thickness Matters: Thinner wheels provide efficient cutting but are more fragile.
- Material Compatibility: Use aluminum cutting wheels for aluminum; avoid aluminum oxide to prevent glazing.
- RPM Verification: Always check RPM compatibility between the wheel and grinder to prevent shattering.
- Match Grain Type: Choose the right grain type for the material; zirconia alumina is best for heavy-duty tasks, while ceramic grains excel in aggressive cutting.
Ignoring Safety Gear
Neglecting to wear the appropriate safety gear can lead to serious injuries while using cut-off wheels. Always equip yourself with personal protective equipment (PPE) like safety goggles, gloves, and a face shield to shield against flying debris and sparks. Inspect your cutting wheel to confirm it’s rated for your grinder’s RPM to avoid shattering.
| Safety Gear | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Safety Goggles | Protects eyes from debris |
| Gloves | Shields hands from cuts and burns |
| Face Shield | Guards face from sparks and debris |
| Guards | Prevents debris from reaching you |
| Inspected Wheels | Reduces risk of catastrophic failure |
Keep flammable materials away from the cutting area, and verify the workpiece is securely clamped.
Applying Excessive Pressure
While using cut-off wheels, it’s crucial to avoid applying excessive pressure, as this can lead to premature wear and damage. Maintaining a steady, light pressure guarantees safe cutting and maximizes wheel lifespan. Here are key points to remember:
- Thinner cut-off wheels (0.04 to 0.045 inches) are designed for precise cuts but can shatter under excessive pressure.
- Overheating can occur with too much pressure, damaging both the wheel and the workpiece.
- A narrow kerf enhances cutting speed but is more vulnerable to damage.
- Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended pressure and techniques for specific materials.
Best Practices for Using Cut-Off Wheels Effectively
To achieve ideal results when using cut-off wheels, you must carefully consider several essential practices. Start by selecting the right type and thickness of your cut-off discs; thinner wheels are perfect for precise cuts, while thicker wheels offer durability for tougher jobs. Always verify the RPM rating of your cut-off wheel matches or exceeds that of your angle grinder to maintain proper safety. Equip yourself with safety gear, like gloves and eye protection, to defend against flying debris. When cutting, apply steady pressure without excessive force to prevent disc glazing, verifying cleaner cuts with minimal burrs. Additionally, always securely clamp your workpieces to minimize movement, enhancing cutting accuracy and promoting safer operation. By following these guidelines, you can liberate your cutting experience, achieving both efficiency and safety in your projects.
Choosing the Right Accessories and Tools for Optimal Performance
Achieving ideal performance with cut-off wheels hinges not just on best practices but also on selecting the right accessories and tools. Choosing the correct cutting disc type is essential; for instance, Type 1 is great for general cuts, while Type 27 excels in flush cutting.
Achieving optimal cut-off wheel performance requires selecting the right tools and accessories for your specific cutting needs.
Consider these key factors:
- Wheel Thickness: Thinner wheels (0.04 to 0.045 inches) offer precision, whereas thicker wheels (over 1/4 inch) are more durable for heavy material removal.
- RPM Rating: Always match the wheel’s RPM with your grinder’s rating to prevent accidents.
- Abrasive Type: Use ceramic grains for aggressive cuts or aluminum oxide for general purposes to enhance cutting speed and reduce wear.
- Safety Accessories: Incorporate guards and backing pads to protect against sparks and debris during cutting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Best Thickness for Cut-Off Wheels?
For ideal cutting, choose a wheel thickness that balances durability and precision, considering factors like material compatibility and heat generation. Always follow manufacturer recommendations while evaluating cost versus performance and prioritizing safety precautions during use.
What Is the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 41 Cut-Off Wheels?
Type 1 wheels excel in general applications, while Type 41 offers advantages in cutting speed and precision. Consider material compatibility, safety, and lifespan when choosing, as costs vary based on performance and user preferences.
What Does the Type Mean on a Cut-Off Wheel?
The type on a cut-off wheel indicates its shape and use, affecting performance in metal cutting applications. Consider wheel diameter, speed ratings, and materials for safety and efficiency, while weighing cost and resin bond advantages.
Are Thicker or Thinner Cutting Discs Better?
Thicker cutting discs offer better durability and heat resistance, making them ideal for demanding materials, while thinner discs enhance cutting efficiency and precision. Your choice should balance performance longevity, application suitability, and safety standards.
Conclusion
In the world of cutting, your angle grinder’s cut-off wheel is your trusty sword. By understanding the types, thickness, and materials, you’re not just equipped; you’re empowered. But remember, safety is your shield—never underestimate the importance of precautions. With the right choices and practices, you’ll slice through projects like a hot knife through butter. So gear up, stay vigilant, and let your creativity flow, knowing you have the knowledge to cut safely and effectively.




