When you’re considering whether to use a plasma cutter or a laser cutter, it’s essential to weigh factors like cost, speed, and cut quality. Plasma cutters often come with a lower initial price and are adept at slicing through thicker materials rapidly. However, laser cutters provide unmatched precision and smoother edges at a steeper cost. Each has distinct advantages depending on your project’s specific demands. Which tool will offer the best balance for your needs?
Understanding Plasma Cutting Technology
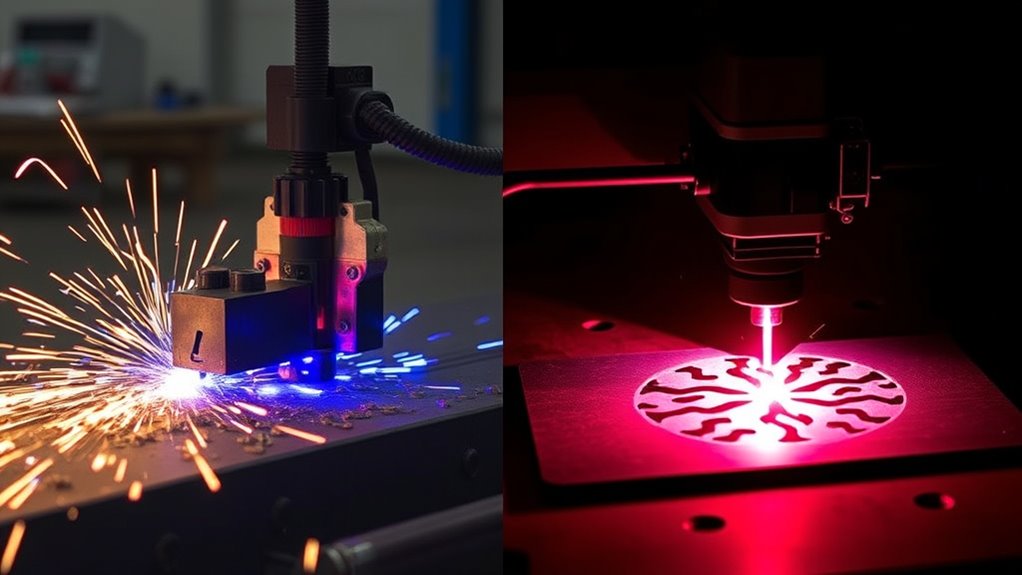
Plasma cutting technology is a precise and efficient method for slicing through electrically conductive materials using a high-velocity jet of ionized gas. By harnessing the power of a plasma arc, this technique achieves temperatures exceeding 20,000°C, effectively melting and cutting through metals such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
The ionized gas, generated by an electric arc, plays a critical role in this process, ensuring rapid heat transfer and efficient material removal.
You can utilize plasma cutting with either handheld torches or automated CNC machines, offering versatility for both manual and industrial applications. While the process produces a larger kerf compared to laser cutting, it compensates by delivering faster cutting speeds, which is ideal for high-volume production.
Despite generating more cutting slag, plasma cutting remains cost-effective, with lower initial investment and operational costs, making it a viable option for various fabrication needs.
Exploring Laser Cutting Technology
When you’re considering laser cutting technology, you’ll find it excels in precision and accuracy, achieving tolerances as fine as ±0.003 mm without burrs.
This method’s versatility is unmatched, allowing you to work with materials like metals, plastics, wood, and ceramics.
Laser cutting also offers impressive speed and efficiency, especially for thinner sheets, making it an ideal choice for detailed and rapid production tasks.
Precision and Accuracy
Although numerous cutting technologies exist, laser cutting stands out for its exceptional precision and accuracy. With tolerance limits as tight as ±0.003 mm, it’s perfect for design intricacy, allowing you to achieve detailed applications that other methods can’t match.
The laser’s focused beam minimizes the heat-affected zone, reducing material distortion and guaranteeing clean, burr-free edges. Here’s what you gain with laser cutting:
- Unmatched Precision: Achieve complex designs with fine detail.
- Minimal Material Distortion: The reduced heat-affected zone guarantees structural integrity.
- Efficient Production: Advanced CNC systems offer rapid, precise movements for high-volume tasks.
Additionally, laser cutting’s high-quality results require minimal post-processing, considerably lowering material waste.
Embrace this cutting-edge technology for its consistent, high-quality outcomes.
Material Versatility
Beyond precision and accuracy, laser cutting technology also offers remarkable material versatility, making it a go-to solution for diverse applications.
You can effectively cut through various materials such as metals, wood, plastics, and ceramics. This versatility in material selection guarantees its application suitability across different industries.
For metals, fiber laser cutting excels, handling various thicknesses with superior edge quality and minimal heat-affected zones. It’s perfect for intricate designs, achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.003 mm.
However, be aware that highly reflective materials like copper and brass might pose operational challenges.
Additionally, the ability to engrave and mark enhances its functionality, allowing for both functional and decorative applications, further broadening its spectrum of uses in manufacturing and design.
Cutting Speed
Laser cutting technology boasts exceptional cutting speeds, a key factor in its efficacy for processing thin materials.
You’ll find that laser cutting techniques can achieve speeds of up to 30 meters per minute, especially when dealing with thin sheets. This rapid pace is complemented by the precision of fiber lasers, which outperform traditional CO2 systems through faster beam delivery and superior beam quality.
Several factors influence speed variations:
- Material Thickness: Thinner materials are cut more swiftly than thicker ones.
- Material Type: Different materials require different power levels for peak cutting.
- Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): Minimal HAZ preserves material integrity, allowing for faster, quality cuts.
Laser cutting’s ability to maintain high speeds without sacrificing quality makes it a top choice for intricate and efficient projects.
Comparing Cutting Precision and Accuracy
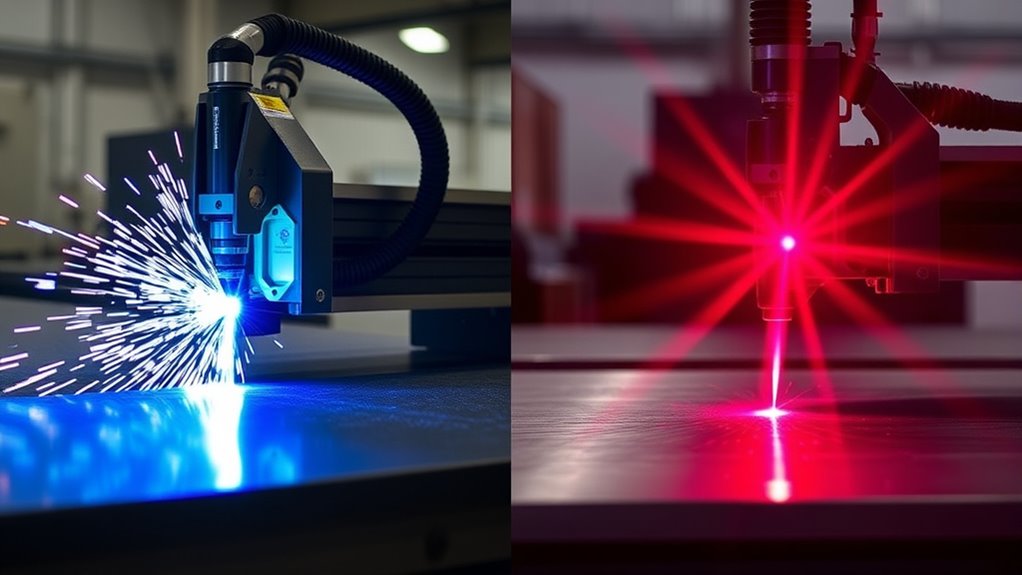
When evaluating cutting technologies, precision and accuracy are paramount factors to contemplate. In a precision comparison, laser cutting consistently outperforms plasma cutting. It offers cutting accuracy with tolerances as precise as ±0.003 mm, making it ideal for intricate designs. Plasma cutting, with tolerances around ±0.1 mm, is less precise but still effective for specific applications.
| Attribute | Laser Cutting | Plasma Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | ±0.003 mm | ±0.1 mm |
| Kerf Width | Narrower | Wider |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, burr-free | Rougher, may need finishing |
| Material Thickness | Up to 25 mm | Up to 38 mm |
The narrower kerf width in laser cutting leads to minimal material waste and clean edges. Additionally, laser cutting produces smoother, burr-free cuts, whereas plasma cutting often necessitates extra finishing due to rougher edges. However, plasma cutting excels with thicker materials, capable of handling up to 38 mm, offering versatility for heavier applications.
Evaluating Speed and Efficiency

When evaluating cutting speed and efficiency, consider that plasma cutters excel in thicker materials with cutting rates of 20-30 inches per minute, while laser cutters outperform in thinner sheets, achieving speeds of 100-200 inches per minute.
Plasma systems enhance efficiency in high-volume scenarios by rapidly processing thicker sections, but laser cutters offer cleaner edges and tighter tolerances, reducing the need for additional finishing.
While plasma cutting is cost-effective for thicker materials, laser cutting’s precision and minimal waste can offset its higher operational costs in environments where material handling and intricate designs are essential.
Comparison of Cutting Speed
Although both plasma and laser cutting techniques offer distinct advantages, evaluating their cutting speed reveals key differences in their efficiency.
When analyzing speed nuances, you’ll find plasma cutting excels with thicker materials, cutting through up to 38 mm with impressive speed. In contrast, laser cutting is more efficient for thin materials, performing best on sheets up to 25 mm.
Consider these points:
- Thicker Materials: Plasma cutting is faster for thicker metals, making it ideal for high-volume industrial applications.
- Thinner Materials: Laser cutting provides superior speed and precision, especially for intricate designs with tighter tolerances.
- Material Waste: The kerf width of plasma cutting is larger, leading to more material waste and extended cleanup times.
Understanding these factors helps in choosing the right technique for your project.
Efficiency in Material Handling
Examining the cutting speed highlights considerable differences between plasma and laser technologies, yet their efficiency in material handling offers further insights into their operational advantages.
Plasma cutting excels with thicker materials, achieving high speeds up to 38 mm, but it struggles with material wastage due to a larger kerf width. This results in less efficient use of raw materials.
In contrast, laser cutting shines with thinner materials and intricate designs, providing cleaner edges that minimize post-processing and cleanup requirements. Its precision reduces material wastage considerably.
While plasma systems require additional cleanup, impacting overall workflow efficiency, laser systems streamline production.
Your choice between these technologies should consider the balance between cutting speed, material thickness, and the associated cleanup and material wastage implications.
Examining Material Compatibility

Material compatibility plays a pivotal role in determining the suitability of plasma and laser cutting technologies for specific applications.
When considering material applications, you should assess the types of metals involved. Plasma cutting excels with conductive metals like steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, accommodating thicker sections up to 38 mm.
In contrast, laser cutting is versatile, handling metals and non-metals, but struggles with reflective surfaces such as copper and brass.
Key Considerations:
- Metal Types: Plasma is advantageous for conductive metals, while laser cutting works with a broader range, including non-metals.
- Thickness: Plasma is best for thicker materials, while laser is ideal for precision in thinner sections up to 25 mm.
- Surface Finish: Laser cutting offers superior finishes and minimal heat-affected zones, perfect for high-quality cuts, whereas plasma might require additional finishing due to rougher edges.
Analyzing Cost and Operational Expenses

When exploring the cost and operational expenses of plasma versus laser cutting systems, it’s crucial to weigh the initial investment against long-term operational costs.
Plasma cutters generally require a lower initial investment, with costs ranging from $10,000 to $100,000, making them attractive for budget-conscious operations. In contrast, laser systems range from $50,000 to $500,000, a significant initial outlay.
However, cost analysis reveals that for high-volume production involving thicker materials, plasma’s operational efficiency shines, often leading to lower overall expenses due to reduced maintenance complexity and direct operating costs.
For high-volume, thick material production, plasma cutting offers superior operational efficiency and reduced overall expenses.
Fiber laser systems, despite their precision, incur higher electricity and gas expenses, impacting long-term costs. Their maintenance often requires specialized technicians, unlike plasma systems, which can be managed in-house.
Consequently, if you’re prioritizing cost-effectiveness in thicker material applications, plasma cutting may offer superior operational efficiency, balancing both initial and ongoing expenditures effectively.
Assessing Cutting Thickness and Applications

Determining the ideal cutting thickness and application for your project is essential when choosing between plasma and laser cutters.
Plasma cutting is your go-to for materials over 16 mm (5/8 inch) thick, making it perfect for heavy-duty projects in construction and manufacturing. Its capability extends to cutting metal sheets up to 38 mm, providing versatility for thick materials.
In contrast, laser cutting shines with materials up to 19 mm thick, offering unmatched precision and edge quality for intricate designs, particularly in industries like aerospace and electronics.
Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide:
- Cutting Thickness: Plasma handles thicker materials (up to 38 mm), while laser excels with thinner ones (up to 19 mm).
- Application Industries: Plasma suits construction and manufacturing; laser fits aerospace and electronics.
- Edge Quality: Laser cutting delivers smoother edges with tighter tolerances, ideal for detailed work compared to plasma’s larger kerf size.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Safety Precautions Are Necessary for Plasma and Laser Cutters?
You should always wear protective gear like gloves and goggles. Follow safety protocols by ensuring proper ventilation, checking equipment integrity, and keeping fire extinguishers nearby. Regularly train on emergency procedures to maintain a safe working environment.
How Does Maintenance Differ Between Plasma and Laser Cutters?
You might think maintenance costs are similar, but they’re not. Plasma cutters require more frequent maintenance due to consumable parts, while laser cutters, though initially more expensive, have less frequent maintenance, leading to longer-term savings.
Can Plasma or Laser Cutters Be Used for Non-Metal Materials?
Yes, you can use laser cutters on non-metal materials due to their versatile cutting capabilities and material compatibility. Plasma cutters, however, are typically limited to metals because they require an electrically conductive material to function effectively.
What Environmental Impact Do Plasma and Laser Cutters Have?
You’ll find that both cutters can impact the environment through energy consumption and emissions. Implementing sustainability practices, like optimizing energy use and waste management, can mitigate adverse effects and promote more eco-friendly operations.
Are There Specific Training Requirements for Operating Plasma and Laser Cutters?
Operating these cutters is like conducting a symphony; you need to follow operational guidelines precisely. Certification programs guarantee you’re skilled in safety protocols and technical nuances, providing you with the expertise to handle each machine efficiently.
Conclusion
When choosing between plasma and laser cutters, what’s most important to your project—speed or precision? Plasma cutters are cost-effective and excel in rapidly slicing through thicker materials, offering a robust solution for high-volume tasks. On the other hand, laser cutters provide unmatched precision and smoother edges, perfect for intricate designs and thinner materials, albeit at a higher price. Carefully weigh your needs against these factors to select the cutting technology that aligns best with your operational goals.



